1925–2025: a century of international pharmaceutical law
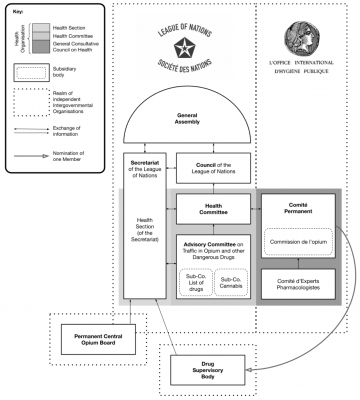
The 1925 Brussels Pharmacopoeia Agreement and Geneva Opium Convention were foundational in shaping international pharmaceutical regulation. The former sought to standardise potent medicines, while the latter established controls over psychoactive substances. Despite differing objectives, both treaties influenced global pharmaceutical governance, contributing to modern regulatory frameworks and standards such as those of WHO or the European Pharmacopoeia. A century later, the year 2025 is witness to turbulent shifts in geopolitics and global health governance, but also revived contemporary debates on drug policy and traditional medicines. This letter revisits the seldom-documented history and impact of international pharmacy law, highlighting the relevance of these two pioneering treaties to evolving pharmaceutical governance and international health law.